
When a product or device fails, you need to know why. Root cause failure analysis helps a business get to the source of a product failure. More importantly, it provides the manufacturer with the information needed to address and correct the issue causing the failure.
Root cause failure analysis is usually a multidisciplinary process. The tools SPM uses during an analysis include visual inspections, metallographic, environmental and chemical analysis and simulation tests. The specific tests utilized depend on the type of product and the failure mode. Root cause failure examinations are designed to determine the cause of the failure and the corrective actions needed to prevent it. However, product failure can be a complicated process. In our experience, device failure is rarely due to a single event.
Typical failure modes involve physical signs of failure, such as a cracked metal component. Various types of corrosion and mechanical damage, are the most obvious. However these signs are often little more than symptoms of failure. SPM looks for the root cause of the failure.
Failure analysis is the process of collecting and analyzing data to determine the cause of a failure, often with the goal of determining corrective actions or liability.
Analysis of a failed part can be done using destructive testing or non-destructive testing (NDT). Destructive testing involves removing a metal component from service and sectioning the component for analysis. Destructive testing gives the failure analyst the ability to conduct the analysis in a laboratory setting and perform tests on the material that will ultimately destroy the component. Non-destructive testing is a test method that allows certain physical properties of metal to be examined without taking the samples completely out of service. NDT is generally used to detect failures in components before the component fails catastrophically.
1. Data Collection
We begin the failure analysis by obtaining background information of the failed component along with manufacturing processes involved, Material used, In-Service Data, if available.
2. Visual Examination
Visual examination of the failure component is a key NDE method to know the failure mode as well as it will reveal the possible damage mechanism. It mainly include inspection of the fracture faces and crack paths, as well as an assessment of abnormal conditions or abuse that the part endured during its service life.

3. Nondestructive Testing, if required
Nondestructive testing can be useful in failure analysis, particularly magnetic particle inspection for ferrous metals, liquid penetrant inspection, and ultrasonic inspection. These inspection methods are used to detect surface cracks and discontinuities. Radiography is used to examine components for internal discontinuities, such as voids and porosity.
4. Identify & mark the samples for further testing
After NDE, the samples are drawn to determine the various testing to be performed on the failed component /s. As per our experience, Visual Examination & Samples drawing are the key & basic steps for more accurate root cause analysis.

A) Macroscopic Examination
Macroscopic examination is an extension of the visual examination and evaluates quality and homogeneity of the part. It is used to determine the origin of the failure and the type of fracture such as ductile, brittle, torsion or fatigue.

B) Mechanical Properties
Mechanical property tests include hardness, tensile and Charpy Impact.
C) Metallographic Examination
Metallographic examination is performed to determine microstructural features such as inclusion content, grain size and rolling direction. These examinations may include optical as well as scanning electron microscopy.
Optical microscopic examination is used to determine grain size, microstructure and inclusion type and content.
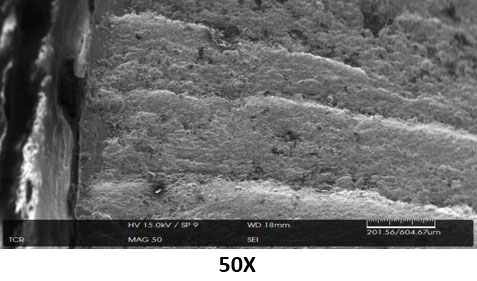
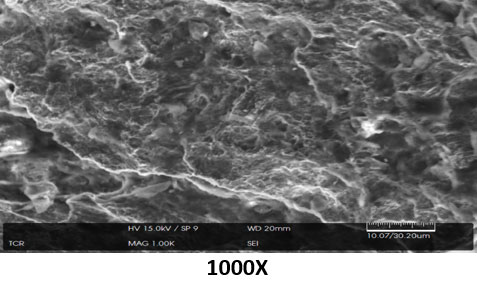
Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) is the scanning of the cracked surfaces under high magnification to get a better understanding of the fracture. It is used to determine abnormalities, such as inclusions, segregation, and surface layers, as well as fracture features and, with the use of Energy Dispersive Spectroscopy (EDS), can identify inclusion type and corrodents on the fracture face.
D) Chemical Analysis
In a failure investigation, chemical analysis is performed routinely to ensure that the material is what was specified.
E) Simulation Tests
Sometimes it may be helpful to determine the root cause of the failure by means of testing that simulates the conditions under which the failure occurred.
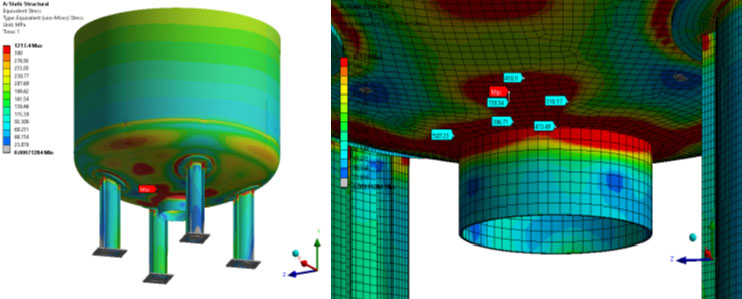
F) Failure analysis by Stress Analyis
We may perform Finite Element Analysis also to determine the root cause analysis of failed component wherein the design of the part or equipment is in question. We follow the client specified Codes / Standards to evaluate the results.
After the completion of the outlined steps, we at SPM interpret and summarize the data that has been collected. In combination, the steps that have been outlined will, in most cases, enable the investigator to conclude the root cause of the failure. Generally the report provides the following:
Many of the recommendations for correcting a problem are small changes that can have a significant impact. Small changes in how source materials and product components are tested, treated and stored can significantly reduce device failure.
In other cases, we find that failure occurs when customers use a equipment or part for too long or in the wrong operating conditions.
We can also help you to determine whether corrective action is necessary. Failure analysis testing can provide you with knowledge needed to make an informed decision.